Table of Contents
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, few innovations have generated as much buzz and potential as blockchain technology. A transformational force in the tech world, blockchain promises to redefine how we conduct transactions, store data, and trust online systems. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a small business owner, or an investor, understanding blockchain can open up new opportunities and insights.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the complexities of blockchain technology, explore its history, explain its workings, discuss real-world applications, and project its future trajectory. By the end of this post, you’ll have a solid grasp of blockchain’s revolutionary potential and how it could impact your world.
Introduction to Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology can be likened to a digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. It ensures that the records are secure, transparent, and immutable. Unlike traditional databases managed by a central authority, blockchain operates on a decentralized network, making it both resilient and reliable.
Central to blockchain’s appeal is its capacity to provide a high level of security. Every transaction recorded on a blockchain is encrypted and linked to the previous one, forming a chain of blocks. This structure makes it extremely difficult for anyone to alter past records without changing all subsequent blocks, which is virtually impossible.
For tech enthusiasts, blockchain represents a fascinating convergence of cryptography, distributed computing, and game theory. For small business owners and investors, it signals a new era of trust and efficiency in commercial transactions and asset management.
History and Evolution of Blockchain
The concept of blockchain technology was first introduced in 2008 with the publication of a whitepaper by an unknown person (or group of people) using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. This document outlined the principles of Bitcoin, the first decentralized cryptocurrency, which was subsequently launched in 2009.
Bitcoin’s success demonstrated the viability of blockchain technology, leading to the development of numerous other cryptocurrencies and blockchain platforms. Ethereum, launched in 2015, introduced the concept of smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. This innovation expanded blockchain’s use cases beyond digital currencies.
Over the years, blockchain technology has continued to evolve. Today, it encompasses various types, including public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, private blockchains used by businesses, and hybrid blockchains that combine elements of both. Each iteration brings new functionalities and potential applications, solidifying blockchain’s role in the future of technology.
How Blockchain Works: Decentralization and Security
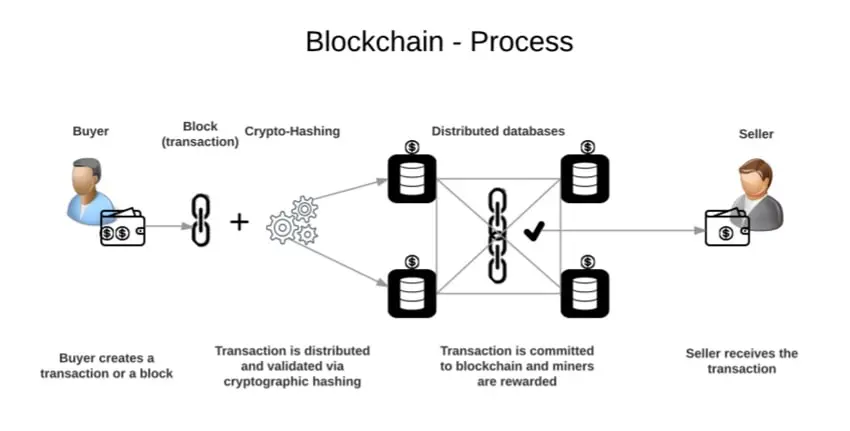
At its core, blockchain technology relies on decentralization and cryptographic security to function effectively. In a decentralized network, multiple nodes (computers) work together to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the ledger. This setup eliminates the need for a central authority, reducing the risk of single points of failure and enhancing the system’s robustness.
Each transaction on a blockchain is encrypted and grouped into a block. Once a block is filled with transactions, it is added to the chain through a consensus mechanism. The most common consensus mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW), used by Bitcoin, and Proof of Stake (PoS), employed by Ethereum 2.0. These mechanisms ensure that all nodes agree on the validity of transactions, making tampering nearly impossible.
Security is further reinforced by the immutability of blockchain records. Once a block is added to the chain, altering its contents would require changing all subsequent blocks, which demands enormous computational power. This feature makes blockchain an attractive solution for industries that require secure and tamper-proof record-keeping.
Real-World Applications: From Finance to Supply Chain
Blockchain technology’s versatility allows it to be applied across various industries, each benefiting from its unique properties. In finance, blockchain enables faster and more secure transactions. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin offer a decentralized alternative to traditional banking, while blockchain-based platforms facilitate cross-border payments and reduce transaction fees.
In supply chain management, blockchain provides transparency and traceability. Businesses can track products from their origin to the consumer, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud. For instance, Walmart uses blockchain to trace the source of its produce, enhancing food safety and quality control.
Blockchain’s potential extends to other sectors like healthcare, where it can secure patient records, and real estate, where it can streamline property transactions. By leveraging blockchain, industries can achieve greater efficiency, security, and trust in their operations.
The Impact of Blockchain on Businesses and Industries
For small business owners and investors, blockchain technology presents a myriad of opportunities. By integrating blockchain into their operations, businesses can enhance transparency, reduce costs, and improve data security. Smart contracts, for example, can automate complex agreements, saving time and minimizing the risk of human error.
Investors, on the other hand, can explore new avenues for diversification and growth. Blockchain-based assets, such as cryptocurrencies and tokenized securities, offer alternative investment opportunities with the potential for high returns. However, it’s essential to conduct thorough research and understand the risks associated with these investments.
Industries that adopt blockchain technology early stand to gain a competitive edge. By leveraging blockchain’s capabilities, businesses can streamline their processes, build customer trust, and stay ahead in an increasingly digital world. The impact of blockchain is already being felt across various sectors, and its influence is only expected to grow.
Challenges and Future of Blockchain Technology
Despite its immense potential, blockchain technology faces several challenges that need to be addressed. Scalability remains a significant concern, as the current infrastructure of many blockchains struggles to handle large volumes of transactions. Solutions like sharding and layer 2 protocols are being developed to address this issue.
Regulation is another critical challenge. The decentralized nature of blockchain makes it difficult for governments to regulate effectively. Clear regulatory frameworks are needed to ensure the technology’s growth while protecting consumers and maintaining financial stability.
Looking ahead, the future of blockchain technology appears promising. Advances in quantum computing, increased adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi), and the integration of blockchain with other emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) are expected to drive its evolution. By staying informed and adaptable, businesses and individuals can harness the full potential of blockchain in the years to come.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is more than just a buzzword; it’s a transformative force with the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our digital lives. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast eager to explore the latest innovations, a small business owner looking to improve efficiency, or an investor seeking new opportunities, understanding blockchain is crucial.
In this guide, we’ve explored the history, workings, applications, and future of blockchain technology. By grasping these concepts, you’re better equipped to navigate the evolving digital landscape and make informed decisions.
The blockchain revolution is just beginning. To stay ahead, consider exploring blockchain courses, attending relevant conferences, and connecting with experts in the field. Your proactive engagement can help shape the future of this groundbreaking technology.



Pingback: "Mobile Charger Types: Choosing the Best One for you. - RefixTechnology